Hand tools are essential for countless tasks, but using them safely is crucial. This guide provides comprehensive hand tools safety guidelines to help you work confidently and avoid accidents.
Introduction to Hand Tools Safety
Hand tools have been a cornerstone of human ingenuity for millennia. From the earliest stone axes to today's precision-engineered instruments, these tools have enabled us to build, create, and repair with unparalleled dexterity. However, the very qualities that make hand tools so versatile—their sharpness, weight, and mechanical advantage—also make them potentially dangerous if not used correctly.
Consider this: according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, hand tool injuries account for a significant portion of workplace accidents each year. Cuts, punctures, and crush injuries are all too common, often resulting from simple oversights or lack of knowledge. But here's the good news: most of these injuries are entirely preventable with proper safety practices.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the essential hand tools safety guidelines that every user—whether a seasoned professional or a novice DIYer—should know. We'll cover everything from understanding different tool types to mastering safe handling techniques, maintaining your tools, and preparing for emergencies. By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to work safely and confidently, ensuring that your projects are not only successful but also injury-free.
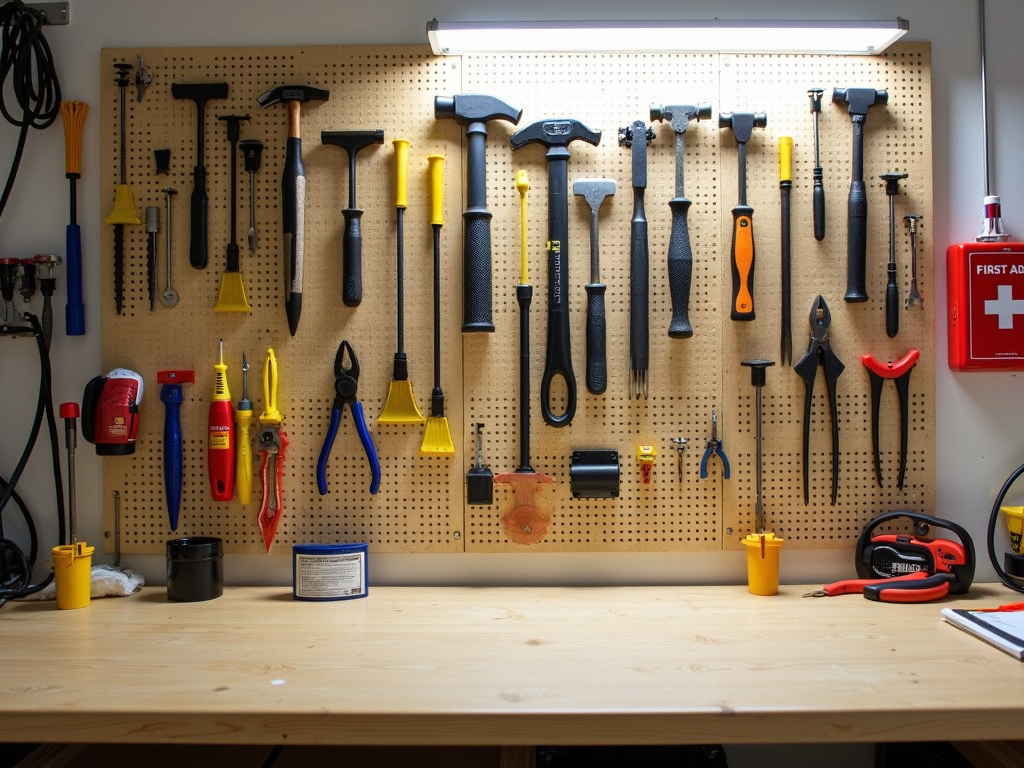

Understanding Different Types of Hand Tools
To use hand tools safely, it's crucial to first understand the various types and their specific risks. Let's break them down:
-
Cutting Tools: These include chisels, utility knives, handsaws, and scissors. Their primary hazard is their sharp edges, which can cause deep cuts or punctures if not handled with care. Always cut away from your body, keep your free hand clear of the cutting path, and use a stable surface to prevent slips.
-
Striking Tools: Hammers, mallets, and sledges are used to deliver forceful blows. The risks here include crushed fingers, flying debris, and even head detachment if the tool is not properly maintained. Ensure that the tool head is securely attached, wear safety glasses to protect against flying particles, and always strike the surface squarely.
-
Measuring Tools: Rulers, tape measures, calipers, and levels are generally safer but can still pose risks if mishandled. For example, a retracting tape measure can snap back and cause injury. Handle these tools with care and store them properly to avoid damage.
-
Fastening Tools: Screwdrivers, wrenches, and pliers are essential for assembly and disassembly. The main risks are slippage, which can lead to abrasions or punctures, and overexertion, which can cause muscle strain. Use the correct size and type of tool for the fastener, and apply steady, controlled force.
By familiarizing yourself with these categories and their associated risks, you can tailor your safety practices to the specific tools you're using.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Hand Tools
Personal Protective Equipment, or PPE, is your first line of defense against hand tool injuries. Here's what you need:
-
Safety Glasses: These protect your eyes from flying debris, dust, and other hazards. Look for glasses that meet ANSI Z87.1 standards for impact resistance.
-
Gloves: Choose gloves that provide a good grip without being too bulky. Leather or synthetic gloves with reinforced palms are ideal for most tasks. Avoid loose-fitting gloves that could get caught in moving parts.
-
Steel-Toed Boots: If you're working with heavy tools or materials, steel-toed boots can prevent crushing injuries to your feet. Ensure they fit well and provide adequate ankle support.
-
Hearing Protection: For noisy environments or when using particularly loud tools, such as pneumatic hammers, use earplugs or earmuffs to protect your hearing.
When selecting PPE, prioritize comfort and fit. Ill-fitting gear can be distracting and may even increase the risk of accidents. Regularly inspect your PPE for signs of wear and replace it as necessary.
For more information on choosing the right PPE, check out the Occupational Safety and Health Administration's (OSHA) guide on personal protective equipment.

Proper Handling and Usage Techniques
Mastering proper handling techniques is essential for safe and effective tool use. Here are some key principles:
-
Use the Right Tool for the Job: It might be tempting to improvise, but using a tool for a purpose it wasn't designed for can lead to accidents. For example, don't use a screwdriver as a pry bar or a wrench as a hammer.
-
Grip and Posture: Hold tools firmly but not too tightly, as excessive grip can lead to fatigue. Maintain a balanced stance, with your feet shoulder-width apart, to ensure stability.
-
Cutting Techniques: When using cutting tools, always cut away from your body. Use a sharp blade to reduce the force needed, and keep your free hand clear of the cutting path.
-
Striking Techniques: With hammers and similar tools, strike the surface squarely to avoid glancing blows. Use controlled, deliberate swings rather than wild, forceful ones.
-
Fastening Techniques: When using screwdrivers or wrenches, apply steady pressure and ensure the tool is properly seated on the fastener. Avoid over-tightening, which can strip screws or damage materials.
One often-overlooked aspect of tool safety is ergonomics. Using tools that fit your hand comfortably and maintaining good posture can prevent repetitive strain injuries. If a tool feels awkward or causes discomfort, consider switching to a different size or style.
For a deeper dive into ergonomic tool use, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) offers excellent resources on workplace ergonomics.
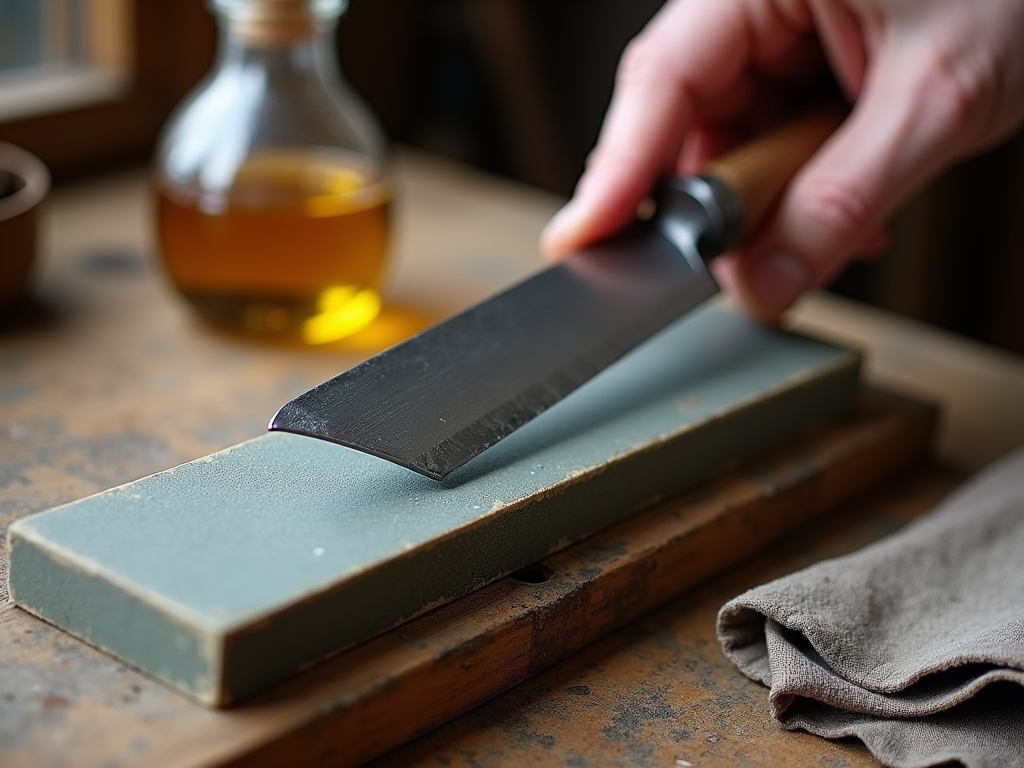

Maintenance and Storage of Hand Tools
Proper maintenance and storage are critical for both safety and tool longevity. Here's how to keep your tools in top shape:
-
Regular Inspection: Before each use, inspect your tools for signs of wear, damage, or looseness. Pay special attention to handles, blades, and moving parts.
-
Sharpening: Keep cutting tools sharp. A dull blade requires more force, increasing the risk of slippage. Use a whetstone, file, or appropriate sharpening tool for the job.
-
Cleaning: After each use, clean your tools to remove dirt, grease, and debris. This not only prevents corrosion but also makes it easier to spot potential issues.
-
Lubrication: For tools with moving parts, such as pliers or adjustable wrenches, apply a light coat of oil to keep them operating smoothly.
-
Storage: Store your tools in a dry, organized manner. Use toolboxes, pegboards, or wall-mounted racks to keep them off the floor and easily accessible. Consider using silica gel packs in your toolbox to absorb moisture and prevent rust.
By taking the time to maintain and store your tools properly, you'll not only extend their lifespan but also reduce the risk of accidents caused by faulty equipment.
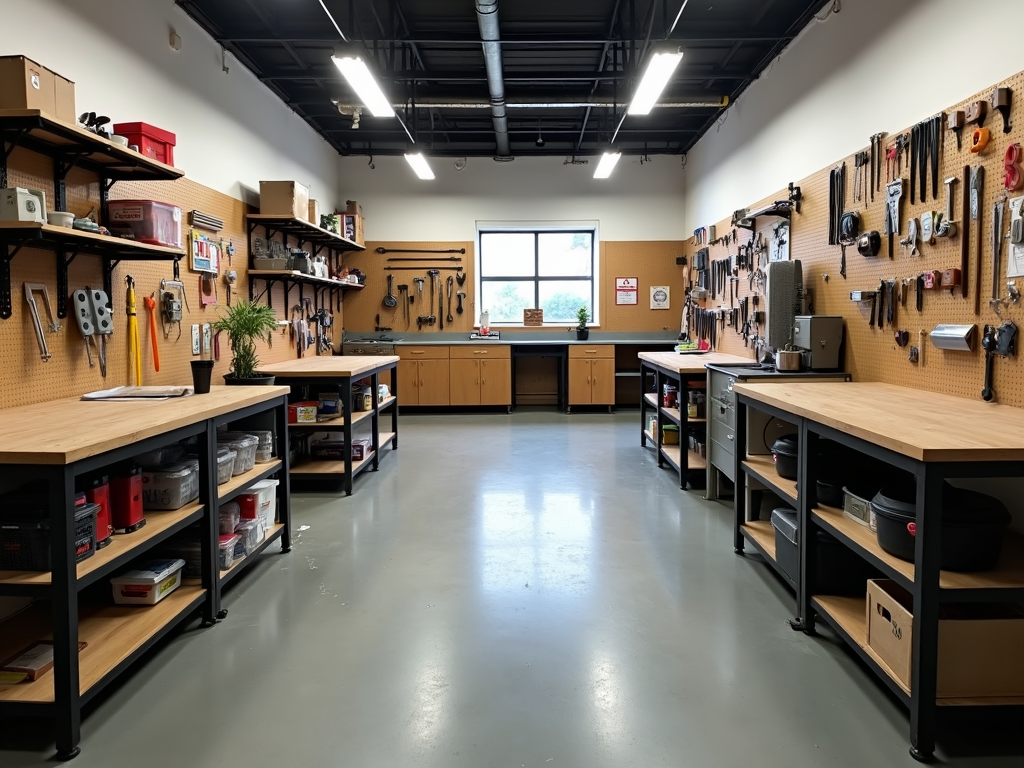

Creating a Safe Work Environment
Your workspace can significantly impact your safety. Here are some tips for setting up a safe and efficient work area:
-
Lighting: Ensure your workspace is well-lit. Poor lighting can lead to eye strain and make it difficult to spot hazards. Use a combination of overhead lights and task lighting for optimal visibility.
-
Organization: Keep your workspace tidy and clutter-free. Designate specific areas for tools, materials, and waste to prevent tripping hazards.
-
Ventilation: If you're working with materials that produce dust, fumes, or vapors, ensure adequate ventilation. Use exhaust fans or work in a well-ventilated area to maintain air quality.
-
Stable Surfaces: Use sturdy workbenches or tables that can support the weight of your projects. Avoid working on uneven or unstable surfaces.
-
Electrical Safety: If you're using power tools in conjunction with hand tools, ensure that electrical cords are in good condition and that outlets are properly grounded.
If you're working with others, establish clear communication protocols. Use verbal cues or hand signals to coordinate actions, especially when handling large or heavy objects.
For more detailed guidelines on workshop safety, the American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP) provides a wealth of resources and standards.
Emergency Preparedness
Even with the best precautions, accidents can still occur. Being prepared can make all the difference in minimizing the impact of an injury.
-
First Aid Kit: Keep a well-stocked first aid kit in your workspace. Include items such as bandages, antiseptic wipes, gauze, adhesive tape, and scissors. Familiarize yourself with the contents and how to use them.
-
Emergency Contacts: Have a list of emergency contacts readily available, including local emergency services and poison control. If you have a medical condition, consider wearing a medical alert bracelet.
-
Training: Consider taking a basic first aid and CPR course. Knowing how to respond to common injuries can be invaluable in an emergency.
-
Fire Safety: If your work involves flammable materials, keep a fire extinguisher nearby and know how to use it. Regularly check smoke detectors and have an evacuation plan in place.
Remember, the key to effective emergency preparedness is not just having the right tools but also knowing how to use them quickly and correctly.
Summary
Hand tools are indispensable for countless tasks, but they demand respect and caution. By adhering to these hand tools safety guidelines, you can protect yourself and others while enjoying the satisfaction of a job well done. Remember to:
- Understand the specific risks associated with different tool types
- Wear appropriate PPE and maintain it properly
- Use correct handling techniques and avoid improvising with tools
- Keep your tools well-maintained and stored safely
- Create a workspace that promotes safety and efficiency
- Be prepared for emergencies with a first aid kit and basic knowledge
Safety isn't a one-time lesson; it's a continuous practice. Make it a habit to review these guidelines regularly and stay updated on best practices. With the right mindset and preparation, you can tackle any project with confidence and skill.
Related hand tools safety guidelines:
- DIY Projects You Can Tackle with Basic Hand Tools
- Best Wrench Sets for Construction Workers: Top Picks for 2023
- DIY Projects: How to Choose the Right Tools for the Job
- Maximizing Efficiency with Smart Toolboxes
- Innovative Workman Tools for Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
- Top 10 Must-Have Tools for Construction Workers
- Choosing the Right Tools for Your Trade
- Must-Have Hand Tools for Every Beginner: A Comprehensive Guide
- Essential Workman Tools for Plumbing and Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide
- What’s New in Workshop Tech for 2024: Innovations Shaping the Future
- The Role of Thermal Imaging in Modern Industry
- Comprehensive Guide to Workman Tools for Beginners











