Overview
Electrical circuits power our world, from lights in your home to the phone in your hand. This guide, Understanding Electrical Circuits: A Beginner’s Guide, makes the basics simple and fun. You’ll learn how circuits work, how to stay safe, and what tools you need to get started.
What is an Electrical Circuit?
Picture water flowing through pipes. The water starts at a pump, travels through tubes, and powers a fountain. An electrical circuit works the same way. Electricity flows from a power source—like a battery—through wires to a device, like a light bulb. It’s a closed loop, meaning the electricity keeps moving in a circle. If the loop breaks, the flow stops, and the light goes out. This is the heart of Understanding Electrical Circuits: A Beginner’s Guide—knowing how electricity moves.
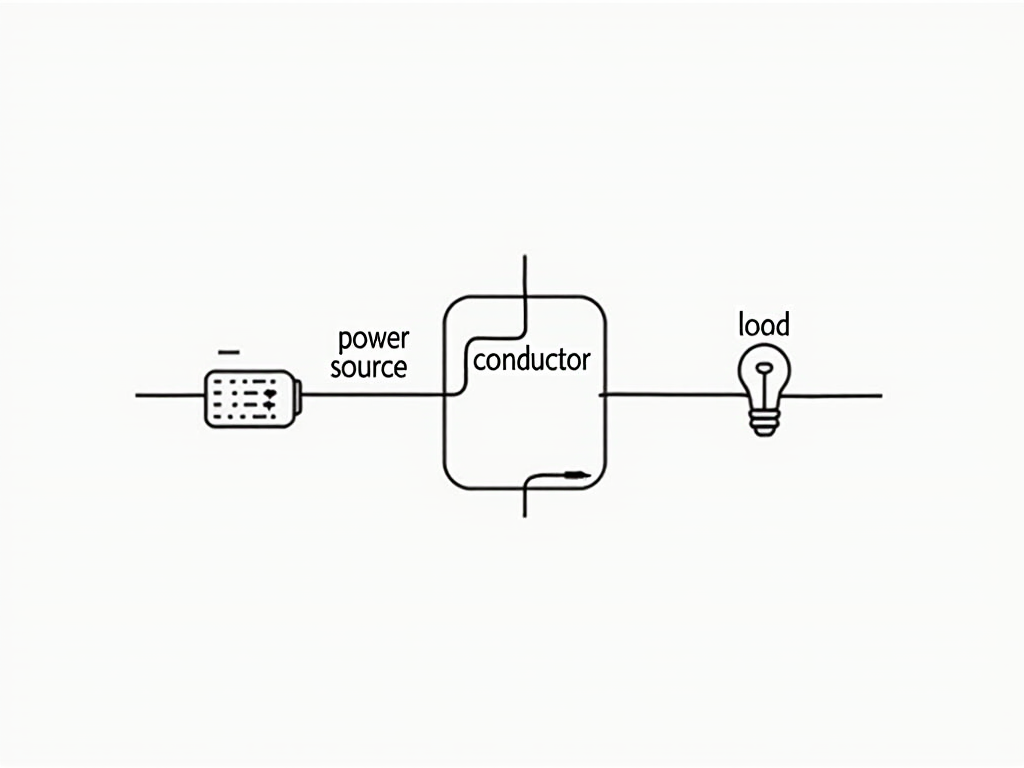
Components of a Circuit
Every circuit needs three things to work:
- Power Source: This is where the electricity comes from. A battery or your home’s electrical outlet does the job. It’s like the push that gets everything moving.
- Conductors: These are the wires. They carry electricity from the power source to the device, acting like pathways.
- Load: This is the device that uses the electricity—a light, a fan, or even a TV. It turns the electricity into something useful, like light or motion.
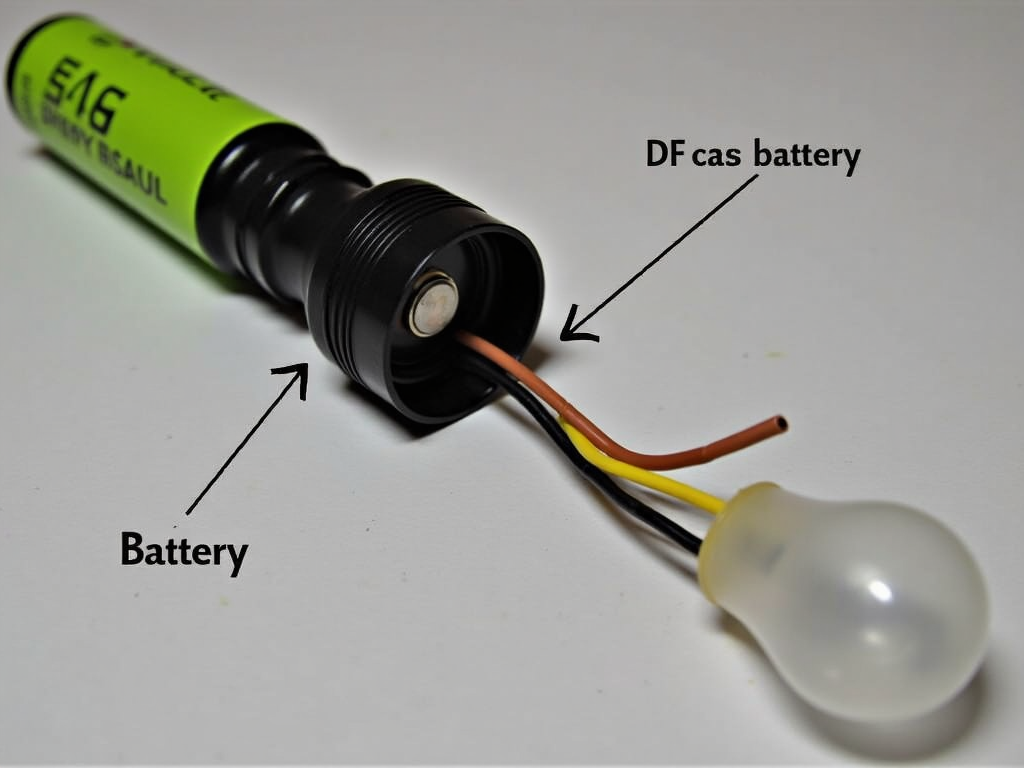
Think about a flashlight. The battery is the power source, the wires inside are the conductors, and the bulb is the load. When you flip the switch, the loop closes, and the light shines. It’s a perfect mini-example of a circuit!

Types of Circuits
Circuits come in two main flavors:
- Series Circuit: Everything connects in one line. Electricity flows through each part one after another. If one piece breaks—like a bulb burning out—the whole circuit stops. Old holiday lights worked this way, which is why one bad bulb could ruin the show.
- Parallel Circuit: This setup has multiple paths. Electricity splits up and flows to different parts at once. If one path fails, the others keep going. Your home uses parallel circuits, so a blown kitchen light doesn’t darken the living room.
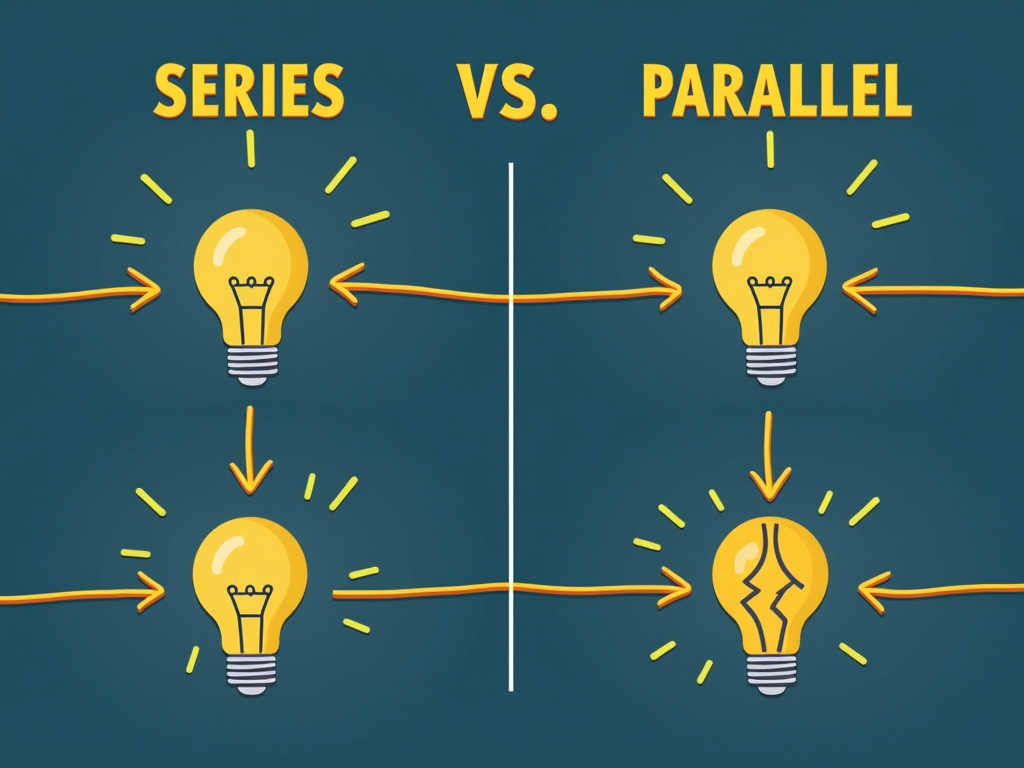
I learned this the hard way when a string of lights went dark at a party. It was a series circuit, and one tiny bulb caused the chaos. Now, I appreciate how parallel circuits keep things running smoothly at home.
Safety Practices in Home Electrical Repairs
Electricity is amazing but can hurt you if you’re not careful. Here are some must-know Safety Practices in Home Electrical Repairs:
- Turn off the power at the breaker before touching anything.
- Use tools with rubber handles—they stop electricity from reaching you.
- Stay dry. Water and electricity don’t mix, so avoid wet floors or hands.
- Wear rubber-soled shoes for extra protection.
The National Fire Protection Association has great tips on staying safe. I once skipped turning off the power and felt a small shock. It scared me enough to never skip that step again.

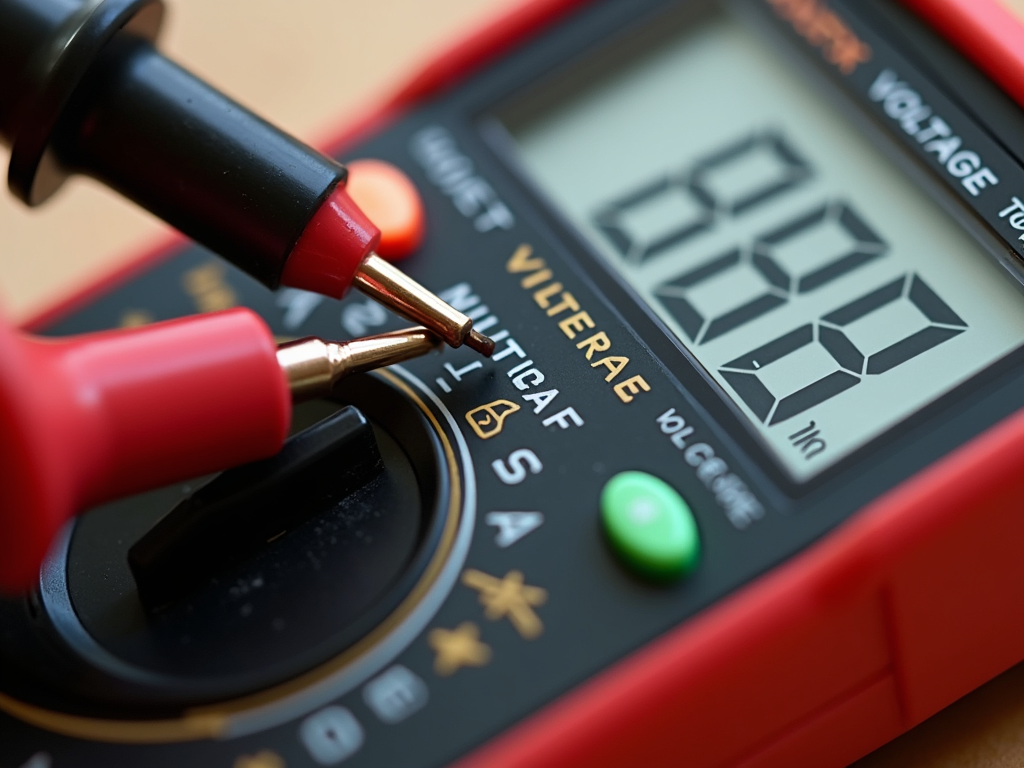
How to Use a Multimeter for Beginners
A multimeter is like a doctor for circuits—it checks voltage, current, and resistance. Here’s How to Use a Multimeter for Beginners:
1. Turn the dial to what you want to measure—say, voltage.
2. Touch the red probe to one spot and the black probe to another. For voltage, go across the part you’re testing.
3. Look at the screen for the number.
It’s easy once you try it. My first time, I tested a battery and felt like a pro when the screen lit up. For more help, see this beginner’s guide to multimeters.

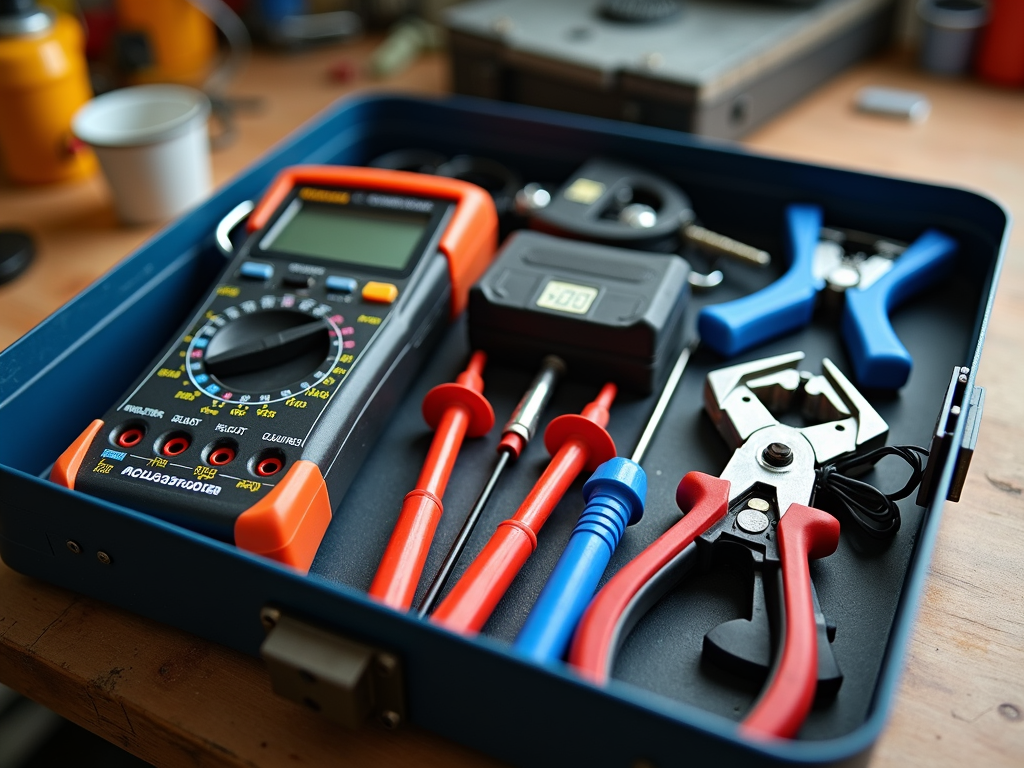
Top 10 Electrical Tools Every Homeowner Needs
Good tools make electrical work simple and safe. Here’s my Top 10 Electrical Tools Every Homeowner Needs:
1. Multimeter – Checks voltage and more.
2. Wire Strippers – Cuts insulation off wires.
3. Screwdrivers – Flathead and Phillips for screws.
4. Needle-Nose Pliers – Grabs small things.
5. Voltage Tester – Shows if wires are live.
6. Electrical Tape – Covers exposed wires.
7. Flashlight – Lights up dark spots.
8. Circuit Tester – Tests outlets.
9. Wire Nuts – Joins wires together.
10. Fish Tape – Pulls wires through walls.
I’ve fixed outlets and lights with these. They’re lifesavers for small jobs.

A Simple Guide to Your Home’s Electrical Setup
Your home’s electrical system might seem tricky, but it’s not. Here’s A Simple Guide to Your Home’s Electrical Setup:
- Electrical Panel: The control center. It sends power to different areas.
- Circuits: Paths that carry electricity to rooms or appliances.
- Outlets and Switches: Where you plug in or turn things on.
Find your panel—usually in a basement or garage. If a breaker trips, flip it back on. I once overloaded a circuit with too many gadgets. Now, I spread out my plugs.
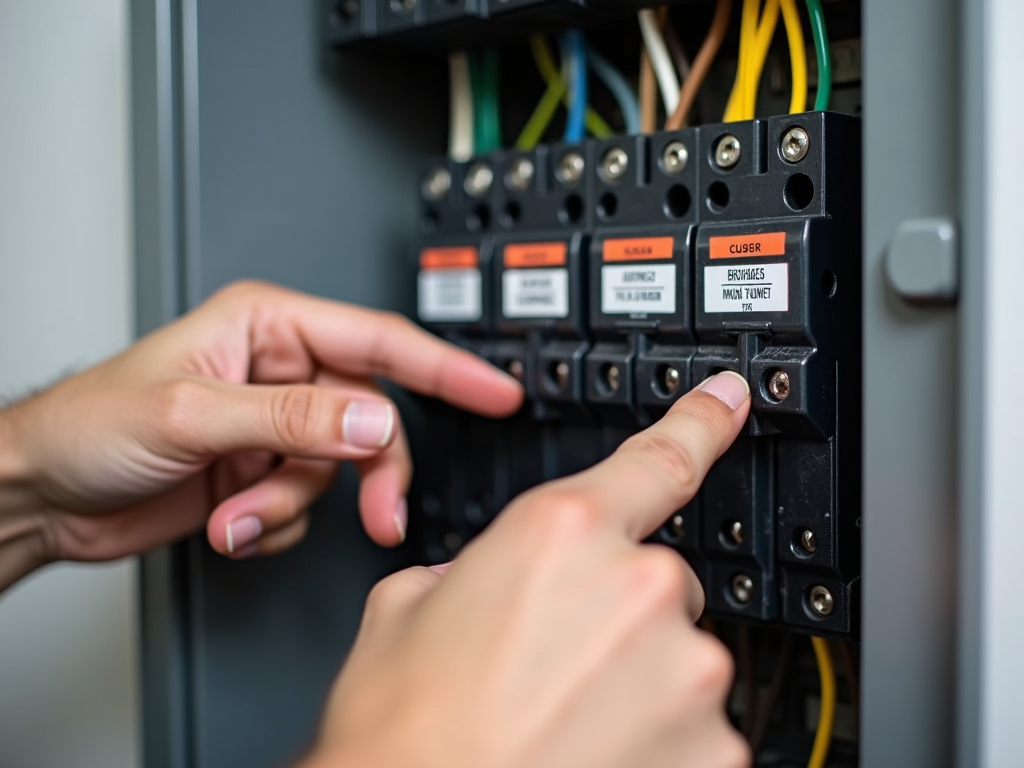

Knowing your setup helps you fix small problems. It’s like knowing where the fuse box is in a car—basic but useful.
Summary
Understanding Electrical Circuits: A Beginner’s Guide is all about starting simple. You’ve learned what circuits are, their parts, and how to stay safe. With the right tools and a bit of know-how, you can handle basic repairs and feel confident. Keep safety first, and you’re set!
Related Understanding Electrical Circuits: A Beginner's Guide:
- The Importance of Tool Safety
- The Rise of Smart Tools in Woodworking: A New Era of Safety and Innovation
- The Ultimate Guide to Power Tools for Precision Drilling
- Best Power Drills for Home Use
- Essential Tools for Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide
- Maximizing Small Workshop Spaces: A Workman's Guide to Efficiency
- Ergonomic Wrenches for Reducing Hand Strain: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Evolution of Workman Tools: From Past to Present
- Understanding Torque Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide
- Top 10 Essential Tools for Every DIY Enthusiast
- Essential Wrenches for Automotive Repair: A Mechanic’s Guide
- Choosing the Right Drill Bits for Electrical Installations: A Comprehensive Guide









